Help your advanced-level students speak about complicated issues like climate change, science and human impact on the earth. This vocabulary set is long, so you should only teach a few words per session.
Don’t forget to practice the target language by asking your student to:
- Give you an example using each piece of vocabulary.
- Practice words and phrases by giving the opinions on certain issues.
- Explaining diagrams and pictures.
This vocabulary set contains two picture worksheets as well as five questions related to the environment.
Science
Testing a theory
To prove – to determine that a theory is correct through testing.
To test, to do a test – a procedure intended to establish the quality, performance, or reliability of something.
To trial, to do a trial – to do a series of tests or to test something for a long time.
‘The drug trial proved that the drug was effective in treating autoimmune disorders.’
Water
To boil – water reaches 100 degrees celsius.
‘You must boil an egg in water for at least two minutes to cook it properly.’
To freeze – water reaches zero degrees celsius.
To melt – when ice warms and turns to water.
To spill – when a liquid is released from its container accidentally.
Irregular verb: Spill, spilt, spilt.
‘Oh no, I have just spilt coffee on my computer!’
To turn into steam – water vapour when water boils.
To turn to ice – ice blocks when water freezes.
‘The lake turns to ice in winter.’
Organs
Brain, heart, lungs, intestines, liver, kidneys, stomach.
Speaking practice
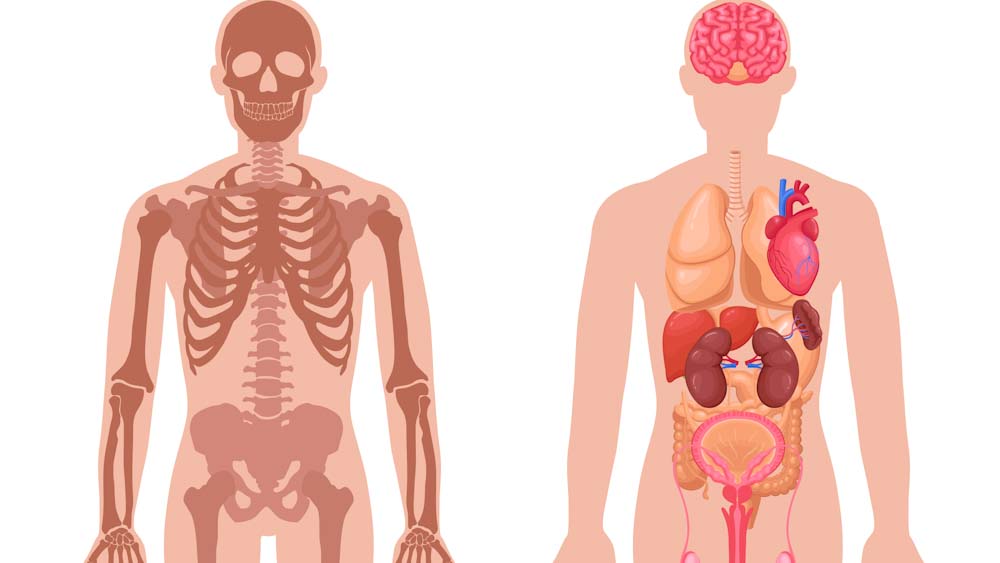
Ask your student to name these organs and bones.
PDF download of interior body diagram
Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto (which is now an asteroid)
Environment
Climate change
Atmosphere – the combination of gasses that cover a planet.
Carbon footprint – the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere as a result of the activities of a particular individual, organization, or community.
‘The European union has pledged to reduce its carbon footprint by 2025.’
Climate change deniers – people who don’t believe that climate change is happening.
‘There are very few climate change deniers outside of US politics.’
Energy consumption – the amount of energy a person, country or organisation consumes.
Fossil fuels (oil, coal, gas) – traditional fuels made from carbon sources.
‘Fossil fuels are slowly being phased out in the UK.’
Global warming – the warming of the earth.
The greenhouse effect – when the Earth’s atmosphere becomes thick with gases and substances which trap the sun’s radiation, making the Earth warmer.
Ozone layer – the layer in the stratosphere which absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation reaching the earth from the sun.
‘There is a hole in the ozone layer above Australia.’
Polar ice caps melting – the ice caps turning to water due to global warming.
‘Polar ice caps are melting at the fastest rate ever.’
Speaking practice
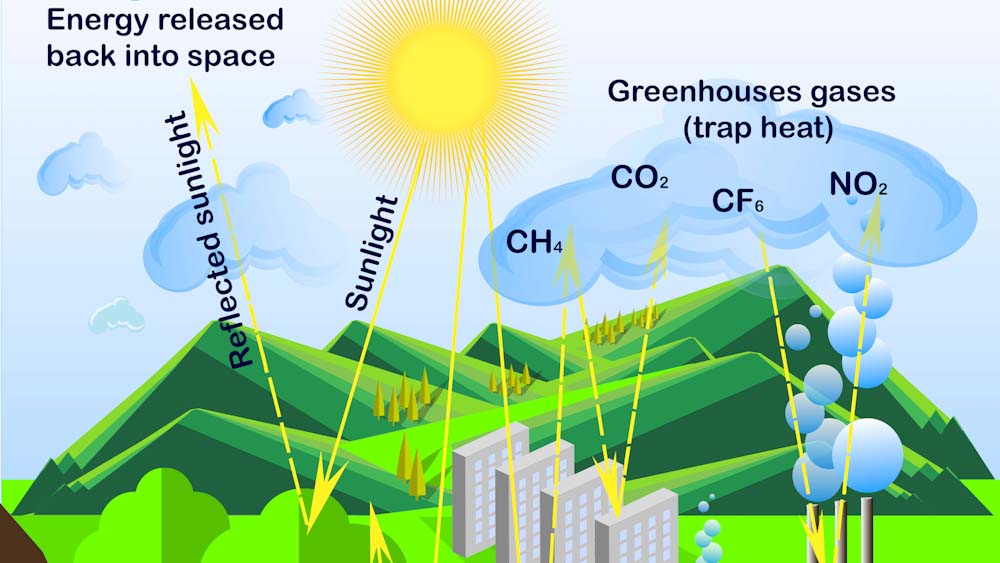
Ask your student to explain this diagram to you.
PDF download the greenhouse effect
Renewable energy
Solar power
Solar panels – the panels that convert sunlight into energy.
Wind power
Hydro power
Other problems
Intermediate
Car exhaust fumes – the gases that cars emit.
To be overpopulated/ overpopulation – too many people.
To emit harmful gases, emissions – to release gases into the environment.
To pollute, pollution – to contaminate.
Toxic – poisonous.
‘Nuclear power stations produce toxic waste.’
Water shortage – a scarcity of water.
‘A bi-product of climate change will be water shortages in countries with warmer climates.’
Advanced
Domestic waste/household waste – the amount of packaging, excess food and other waste a family produces.
To dump rubbish/ trash – to ‘throw away’ trash in large quantities.
‘Companies have been known to dump toxic waste into rivers.’
Landfill – a large hole in the ground where people dump rubbish.
‘Non-recyclable waste goes into a landfill.’
Oil spillage – when a large amount of oil is accidentally released into the sea.
Oil tanker – a ship carrying oil.
Animals
An endangered species – a species which is very rare.
To become extinct / to die out – when a species ceases to exist.
‘The dodo became extinct two hundred years ago.’
Habitat – the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, insects – types of organisms.
To lay an egg – not ‘to put an egg.’
‘Birds, insects, fish and reptiles lay eggs.’
Wildlife – the life that exists in the natural world.
Solutions
Intermediate
Environmentalist – someone who works to protect the environment.
To ban – to prohibit.
‘High polluting vehicles are banned in some cities.’
To clean up – to clean an area.
‘We must clean up the plastic in the oceans.
To preserve – to protect a natural area by prohibiting people developing it.
To protest, to do a protest – a manifestation.
‘People are protesting against climate change all around the world.’
Recycling, to recycle.
‘Recycling is becoming more and more popular.’
To reuse – to use again.
‘We should reuse containers to reduce waste.’
Advanced
To combat, to tackle a problem – to fight for a solution to a problem.
‘Governments are trying to combat climate change by switching to renewable energy.’
To pledge – an official promise made by individuals, governments and organisation.
‘The conference ended with a pledge to reduce carbon emissions.’
To reduce, to cut down on – to decrease something.
‘We should all try to cut down on our plastic consumption.’
Forests
To cut down a forest – to cut the trees in a forest.
Forest fires
To catch fire – to ignite a fire.
To put out a fire / to extinguish a fire.
‘Forests catch fire easily in summer. It often takes days to put them out.’
Timber – the wood product after a tree is cut down.
‘Timber houses are rare in the UK but common in Norway.’
Extreme weather
Blizzard – snowstorm
Hurricane – a windstorm.
Typhoon – tropical storm.
To flood, a flood – an inundation of water.
‘The river overflowed in the rainstorm and caused a flood.’
Drought – when it doesn’t rain for a long time and the land becomes so dry that plants can’t grow.
‘One summer there was no rain and so there was a terrible drought.’
Water shortage – a scarcity of water.
Sandstorm – a storm of sand.
Phrases
The tip of the iceberg – the small perceptible part of a much larger situation or problem that remains hidden.
‘Carbon emissions from cars is only the tip of the iceberg. There are many more things, including farm animals, that emit CO2.’
To take for granted – tofail to appreciate someone or something because you think that it will always be there.
‘We take the land for granted.’
To be the hardest hit – to be severely affected by something.
‘People in the developing world are hardest hit by climate change because they live in warm countries.’
To rely on something, to be reliant on something – to need something.
‘We are still reliant on fossil fuels for most of our energy.’
Speaking practice
Use these questions as topics for discussion.
- What are the biggest environmental problems in your region?
- What is the environmental issue that concerns you the most?
- What are the most effective ways that humans can limit their impact on the environment?
- If you were prime minister/president of your country, what policies would you implement to combat climate change?
- How do you think the world will have changed by 2050?
Final thoughts and homework
How long will Human Impacts Last? is a short TED ed film about how we are now living in a new geological age called the Anthropocene, meaning human activity can now be found in the planet’s geology.

